Table of Contents
In the world of cryptocurrency trading, arbitrage has emerged as a very popular strategy among traders that allows them to capitalize on market inefficiencies while minimizing risk. It has emerged as one of the most reliable ways to profit from digital asset markets without taking on significant risk.
What is Crypto Arbitrage?
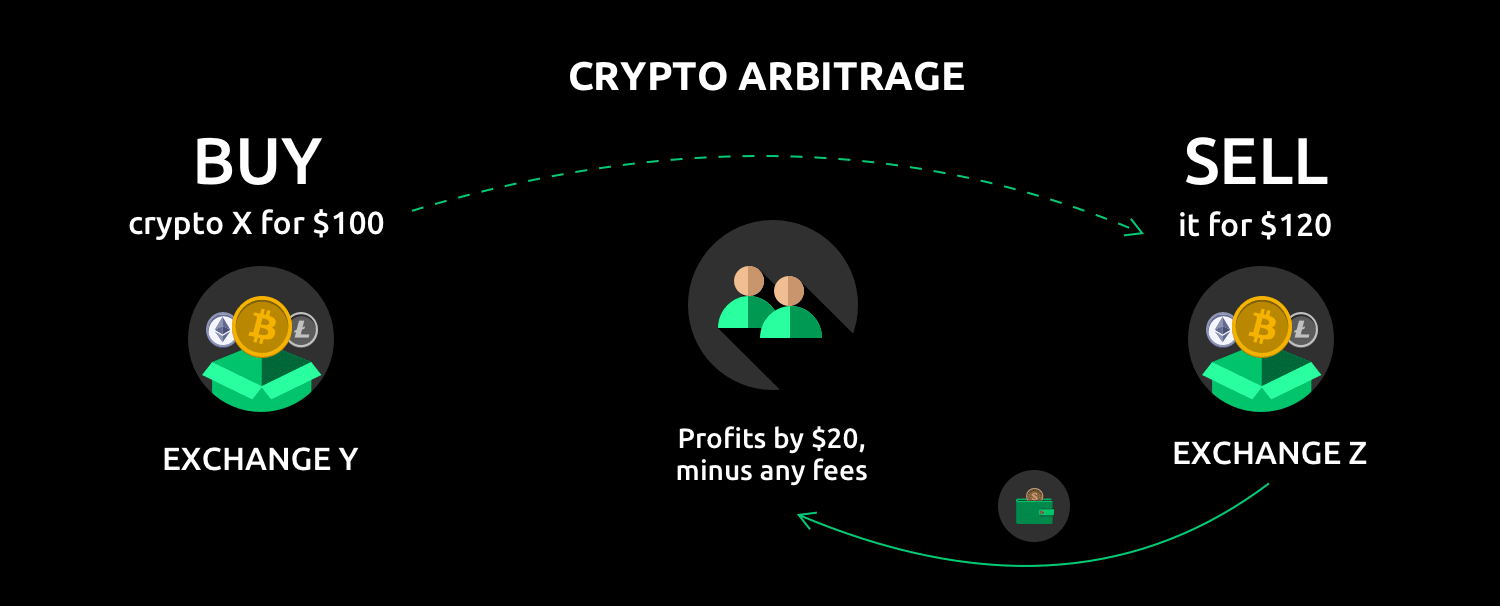
Crypto arbitrage represents a trading strategy that takes advantage of price discrepancies across different cryptocurrency exchanges or markets. These price differences emerge due to varying levels of liquidity, regional market dynamics, and the decentralized nature of cryptocurrency trading. Unlike traditional trading strategies that rely on price speculation, arbitrage focuses on exploiting existing price differences, making it the most lucrative option for risk-aware traders.
Main Types of Crypto Arbitrage
1. Cross-Exchange Arbitrage
Among the various types of crypto arbitrage is Cross-exchange arbitrage which focuses on exploiting price differences of the same asset across different trading platforms. This foundational strategy requires traders to maintain balances across multiple exchanges and execute trades swiftly to capitalize on price disparities. Success in cross-exchange arbitrage depends on sophisticated monitoring systems, efficient capital management, and overcoming various operational challenges such as transfer delays and trading fees.
Standard Arbitrage
One of the sub-types of cross-exchange crypto arbitrage is the standard arbitrage involves the straightforward process of buying cryptocurrencies on exchanges where prices are lower and simultaneously selling them on platforms where prices are higher. For example, if Bitcoin trades at $45,000 on Binance and $45,300 on Coinbase, traders can execute a quick risk-free profit of $300 minus trading fees per Bitcoin. The key to success lies in fast execution and having sufficient balances across exchanges to avoid any last-minute transfer delays that could minimize profits as prices converge.
Spatial Arbitrage
Spatial arbitrage focuses on price differences between exchanges in different geographical regions, often driven by local market conditions and regulatory environments. A prime example is the “Kimchi premium” in South Korean markets, where cryptocurrencies frequently trade at significant premiums compared to global exchanges. This strategy requires understanding regional restrictions, managing currency exchange risks, and navigating local regulatory requirements to effectively capitalize on these geographical price disparities.
Decentralized Arbitrage
Decentralized arbitrage capitalizes on price differences between decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and centralized platforms, or between different DEX protocols. This strategy leverages the unique characteristics of automated market makers (AMMs) and liquidity pools, where prices can deviate significantly from centralized exchange rates. Success requires a deep understanding of DeFi mechanics, gas fee optimization, and quick execution to profit from temporary price misalignments in the decentralized ecosystem. Learn to build a DEX on Sui Blockchain.
AMM vs. CEX Arbitrage
Automated Market Maker (AMM) protocols often have different prices compared to centralized exchanges. Traders can profit from these differences while considering gas fees and slippage.
Cross-DEX Arbitrage
Price differences between different DEXs on the same blockchain network can create arbitrage opportunities. For example, trading between Uniswap and SushiSwap on Ethereum.
Cross-Chain DEX Arbitrage
This involves exploiting price differences between DEXs on different blockchain networks, such as trading between Uniswap (Ethereum) and PancakeSwap (BSC).
2. Intra-Exchange Crypto Arbitrage
Intra-exchange arbitrage occurs entirely within a single exchange platform, eliminating the need for cross-platform transfers and reducing operational complexity. This type of arbitrage focuses on exploiting price inefficiencies between different products or trading pairs available on the same exchange. The strategy requires careful attention to trading fees and platform-specific mechanics to ensure profitable execution.
Funding Fee Futures/Spot Arbitrage
Funding fee arbitrage involves simultaneously holding positions in both futures and spot markets while profiting from funding rate payments. When perpetual futures contracts experience significant imbalances between long and short positions, traders can earn guaranteed returns by taking opposing positions in spot and futures markets while collecting funding payments. This strategy requires precise position sizing and careful monitoring of funding rates to maintain profitability.
P2P Crypto Arbitrage
P2P arbitrage exploits price differences in peer-to-peer markets where traders directly interact with each other. Successful P2P arbitrageurs post both buy and sell advertisements with different prices, profiting from the spread between their purchase and sale prices. The strategy requires careful attention to payment methods, counterparty risk, and platform security while maintaining sufficient margins to cover associated fees and potential risks.
Triangular Arbitrage
Triangular arbitrage exploits price inefficiencies between three different cryptocurrencies traded on the same exchange. This strategy involves executing a series of trades through different trading pairs (for example, BTC/USDT → ETH/BTC → ETH/USDT) to generate risk-free profits when price relationships become temporarily misaligned. Success requires sophisticated monitoring systems and rapid execution capabilities to capture these opportunities before they disappear.
3. Options Trading Crypto Arbitrage
Options trading arbitrage capitalizes on discrepancies between options market prices and underlying asset values, focusing on mathematical relationships and market inefficiencies in derivatives trading. This advanced strategy requires deep understanding of options mechanics, volatility metrics, and sophisticated risk management techniques to execute successfully.
Call Option Strategy
Call option arbitrage involves exploiting discrepancies between the market’s implied volatility and actual price movements of cryptocurrencies. Traders purchase call options when they identify situations where the market has underpriced the probability of significant price movements, potentially profiting when the underlying asset’s volatility exceeds market expectations. This strategy requires careful analysis of volatility metrics and precise timing of entry and exit points.
Put-Call Parity Strategy
Put-call parity arbitrage exploits violations of the fundamental relationship between put options, call options, and the underlying asset price. Traders identify situations where the combined value of put and call options deviates from theoretical values, taking positions that profit when prices return to equilibrium. Success requires sophisticated mathematical modeling and quick execution capabilities to capture these often brief market inefficiencies.
Advanced Risk Management Framework
Successful arbitrage trading requires a sophisticated risk management approach. Market makers and institutional traders typically implement a multi-layered risk framework that includes position limits, exchange exposure limits, and automated circuit breakers. These systems monitor various risk metrics in real time, including:
Exchange health indicators play a crucial role in risk management, as they help traders identify potential issues before they impact trading operations. This includes monitoring exchange uptime, withdrawal processing times, and trading engine performance. Liquidity depth analysis ensures that trades can be executed without significant slippage, while spread volatility monitoring helps identify unusual market conditions that might indicate increased risk.
Counter-party risk assessment is particularly important in crypto arbitrage, as traders often need to maintain significant balances across multiple exchanges. This involves regular evaluation of exchange security measures, insurance coverage, and regulatory compliance status.
Conclusion
Crypto arbitrage represents a sophisticated trading strategy that requires expertise, proper risk management, and sufficient capital. While it offers the potential for consistent returns with lower risk compared to directional trading, success depends on careful implementation and continuous monitoring of market conditions.
For traders willing to invest in the necessary infrastructure and develop proper risk management systems, crypto arbitrage can provide a sustainable trading strategy independent of the overall market direction. As the cryptocurrency market continues to mature, identifying and capturing arbitrage opportunities will require increasingly sophisticated approaches and robust risk management frameworks.
The key to success in crypto arbitrage lies in maintaining a disciplined approach, continuously monitoring market conditions, and having the patience to wait for genuine opportunities while avoiding the temptation to force trades when conditions are suboptimal.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
What is the minimum capital needed to start crypto arbitrage?
While it’s technically possible to start with a few thousand dollars, professional arbitrage trading typically requires a minimum of $50,000 to generate meaningful returns. This amount allows traders to overcome transaction fees and maintain sufficient balances across multiple exchanges.
How do I handle cryptocurrency network delays?
Network delays can be mitigated by maintaining balanced positions across exchanges and using stablecoins for transfers when possible. Additionally, implementing a cross-exchange netting system can help minimize actual cryptocurrency transfers.
Are arbitrage profits guaranteed?
While arbitrage opportunities represent price inefficiencies rather than speculative positions, profits are not guaranteed. Execution risk, exchange risk, and network delays can all impact the profitability of arbitrage trades.
How do I calculate the true cost of arbitrage trades?
The total cost calculation must include: Exchange trading fees, withdrawal fees, network transaction fees, spread costs, potential slippage, and currency conversion fees (if applicable) all need to be carefully considered before executing any arbitrage strategy.
What skills are needed for successful crypto arbitrage trading?
Successful crypto arbitrage trading requires a combination of market knowledge, risk management expertise, and attention to detail. Traders should have a strong understanding of cryptocurrency markets, exchange mechanics, and trading operations.