Table of Contents

Beam Chain was one of the major announcements that took the stage during Devcon Bangkok 2024. Justin Drake, one of the core contributors at Ethereum, made the announcement, but the market did not seem to be very happy about it. While the press conference was going on, the price of Ethereum fell sharply. However, he confirmed that it is just a proposal at the moment and a consensus needs to be reached to bring it into existence. Let us look at what is Beam Chain and how will it add value to the Ethereum Ecosystem.
History of Upgrades
Ethereum’s path has been marked by various upgrades that have enhanced its capabilities and strengthened the community as a whole. Each step has built upon the last from its genesis in 2015 through the historic Merge in 2022. The introduction of the Beacon Chain in 2020 revolutionized Ethereum’s consensus mechanism, laying the groundwork for proof of stake and setting the stage for future innovations. Read more about the previous upgrades here.
The Beacon Chain Foundation
The Beacon Chain represented Ethereum’s first major step toward a more sustainable and scalable future. It was launched in December 2020, which then introduced the proof-of-stake consensus mechanism that would eventually replace Proof of Work and was called Ethereum 2.0. With its 32 ETH staking requirement, 12-second block times, and sophisticated validator system, the Beacon Chain served as the backbone for Ethereum’s most significant transition to date – The Merge.
The Beacon Chain was a chain of ’empty’ blocks, but switching off proof-of-work and switching on proof-of-stake on Ethereum required instructing the Beacon Chain to accept transaction data from execution clients, bundle them into blocks and then organize them into a blockchain using a proof-of-stake-based consensus mechanism. At the same moment, the original Ethereum clients turned off their mining, block propagation, and consensus logic, handing that all over to the Beacon Chain.
Once The Merge happened, there were no longer two blockchains. Instead, there was just one proof-of-stake Ethereum, which now requires two different clients per node. The Beacon Chain is now the consensus layer, a peer-to-peer network of consensus clients that handles block gossip and consensus logic. In contrast, the original clients form the execution layer, which is responsible for gossiping and executing transactions and managing Ethereum’s state. The two layers can communicate with one another using the Engine API.
The Need for Change
At Devcon 2024 in Bangkok, Justin Drake unveiled what he called Ethereum’s “most ambitious” consensus layer change – the Beam Chain proposal. The timing of this announcement reflects a critical realization: the Beacon Chain, while revolutionary, is showing its age. As Drake explained, “Specifications were frozen five years ago, and a lot has changed in those five years, especially since our understanding of new perspectives is much deeper than it was five years ago.”
Over the past five years, there have been numerous breakthroughs in SNARKs technology, increasing speeds by orders of magnitude. At the same time, the community has also experienced the birth of zkVMs, an amazing technology that allows any programmer in the world to take advantage of this powerful technology without needing to be versed in cryptography or have a deep understanding of SNARKs.
Understanding the Differences
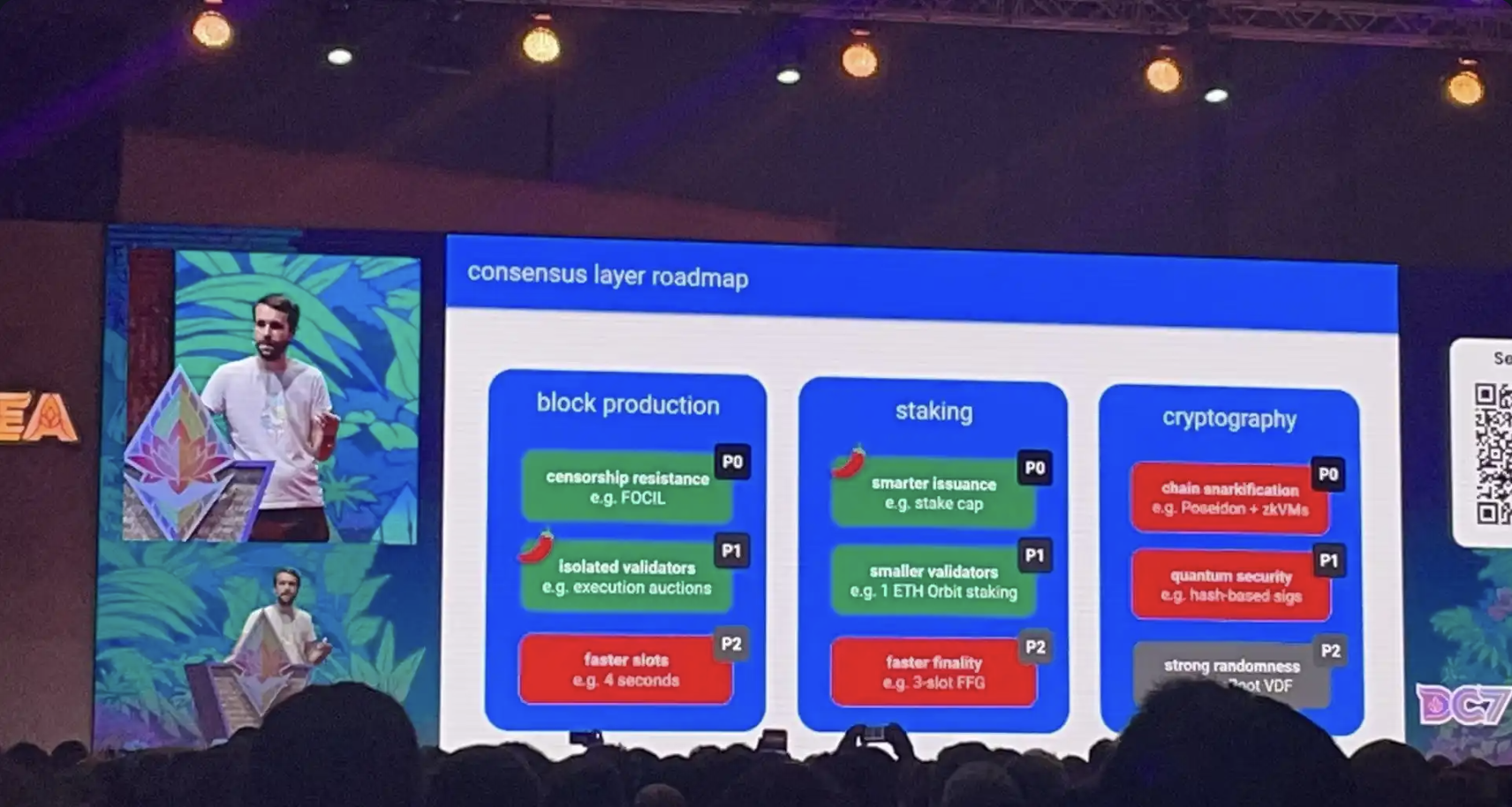
The transition from Beacon to Beam Chain represents a fundamental evolution in how Ethereum’s consensus works. Where the Beacon Chain established proof of stake, Beam Chain aims to perfect it. The key differences emerge in several crucial areas:
The Beacon Chain relied on a more rigid structure with a 32 ETH staking requirement, creating a barrier for many potential validators. Beam Chain proposes to dramatically lower this threshold to 1 ETH, democratizing network participation. Where Beacon Chain established basic block production mechanisms, Beam Chain introduces sophisticated “inclusion lists” and proposer-builder separation (PBS) to enhance censorship resistance and reduce MEV-related issues.
Perhaps most significantly, while Beacon Chain focused on establishing fundamental proof-of-stake operations, Beam Chain leverages advanced cryptographic technologies, including SNARKs and quantum-resistant security measures, preparing Ethereum for long-term sustainability and security.
The Road to Implementation
Drake outlined an ambitious but measured timeline for Beam Chain’s development. Beginning in 2025, a small team of researchers will start the normalization process, carefully laying the groundwork for this massive transition. The development phase will commence in 2026, with client teams writing production-grade code. A thorough testing process is planned for 2027, ensuring the security and stability of the new system before any deployment.
What technology does Beam Chain use?
Beam Chain’s technical architecture introduces several groundbreaking elements. The integration of SNARKs allows for mathematical proof of state transitions without requiring every node to process every computation. The reduction in staking requirements democratizes network participation, potentially leading to greater decentralization. The implementation of quantum-resistant cryptography future-proofs the network against emerging computational threats.
Think of this as different eras of Ethereum’s consensus mechanism: initially the Proof of Work (POW) era, then moving into the Proof of Stake (POS) era, and now we may be entering a Zero Knowledge Proof (ZK) era.
In the ZK era, we will make heavy use of SNARKs technology. One place where we are already using SNARKs is to provide zero-knowledge verification for the entire Beam Chain – the entire consensus layer – and this is where zkVMs (zero-knowledge virtual machines) become very useful. Imagine that we could implement Beam Chain in different high-level programming languages, such as Rust and Go, and then compile these high-level languages into bytecode that zkVMs can understand to achieve SNARK verification without worrying about the low-level details.
One point that needs to be emphasized is that the only part that requires SNARK verification is the State Transition Function, which is the core of becoming a consensus client. Essentially, the state transition function is a very small part of the client build, and surrounding infrastructure (such as networking, synchronization, cache optimization, or block selection rules) does not require SNARK verification.
Beam Chain will implement aggregable signatures. He stated he would like to have quantum-resistant aggregable signatures, and the proposal here is to use hash functions. Hash functions are quantum-resistant and can be used as a basic module for building cryptography.
We will use hash-based signatures, generated by verifiers and provers, and will also introduce hash-based SNARKs that can compress thousands of signatures into a single proof. By combining the two, we can build a quantum-resistant, aggregable hash-based solution that can be used on Ethereum. An interesting detail is that this aggregation scheme has the capability of infinite recursive aggregation, which means that the aggregation results can be continuously re-aggregated, which is currently not possible with BLS signatures and is more flexible.
Looking Ahead

The journey from Beacon to Beam Chain represents more than just a technical upgrade – it’s a reimagining of how Ethereum’s consensus can work in harmony with the latest technological advances. While the development timeline stretches into 2030, the promise of a more accessible, efficient, and secure Ethereum network makes this ambitious proposal a crucial next step in Ethereum’s evolution.
As Drake concluded in his presentation, this is an opportunity to inject new blood into the consensus client and clean up technical debt while implementing cutting-edge technologies. The success of this transition will depend on community support, technical execution, and market acceptance, but the comprehensive nature of the proposal suggests a well-thought-out approach to network evolution rather than a disruptive overhaul.
Conclusion
The Ethereum ecosystem is still at a very young stage with a lot of room for development. The team has laid a 5-year plan for Beam Chain development but they will keep the community informed about the progress. This is a very good opportunity for developers to keep contributing to the Ethereum ecosystem and add to the growth of the community.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Will there be a new network or token launch with Beam chain?
No, The Beam Chain is an upgrade to the consensus layer and no new network or token will be launched with the upgrade.
When will the Beam Chain upgrade take place?
As per the announcement, it is still in the proposal phase, and as per the roadmap, the entire process will be completed by 2030.
Why are we making this upgrade?
As the community believes that the Beacon chain is still relevant, it is 5 years older and does not make use of technologies like ZK, SNARKs, and advanced cryptography.
