Table of Contents
The web3 industry has evolved exponentially over the past decade, leading to a rise in different blockchain networks and infrastructure tools. But with so many L1s and L2s coming into existence we now have created a landscape of isolated blockchain islands that cannot communicate or interact effectively due to compatibility issues. That is where Cosmos comes into the picture—a project that envisions and implements the “Internet of Blockchains” – a network where different blockchain platforms can seamlessly interact while maintaining sovereignty.
Cosmos Vision
In order to unlock the potential of blockchain technology, Cosmos emerged from the understanding that there will not be a single dominant chain, but rather an interconnected network of specialized blockchains. This vision differentiates the traditional monolithic blockchain architecture into a more modular, scalable, and interoperable ecosystem. In the same way that Internet protocols enabled computer networks to communicate, Cosmos intends to standardize blockchain network communication.
The core philosophy behind Cosmos emphasizes three fundamental principles: sovereignty, scalability, and sustainability.
As a result of sovereignty, each blockchain within the network retains complete control over its economic and governance functions. While, scalability is achieved by creating purpose-specific blocks that are capable of handling their own transactions. And sustainability is based on its efficient proof-of-stake consensus mechanism as well as its ability to upgrade chains without disrupting the entire network.
Timeline of Cosmos Ecosystem
The journey of Cosmos began in 2014 when Jae Kwon started developing Tendermint, the consensus engine that would later become the foundation of the Cosmos network. In 2016, the Interchain Foundation (ICF) was established in Switzerland to support the development of the Cosmos ecosystem. Read about the founders in our blog here.
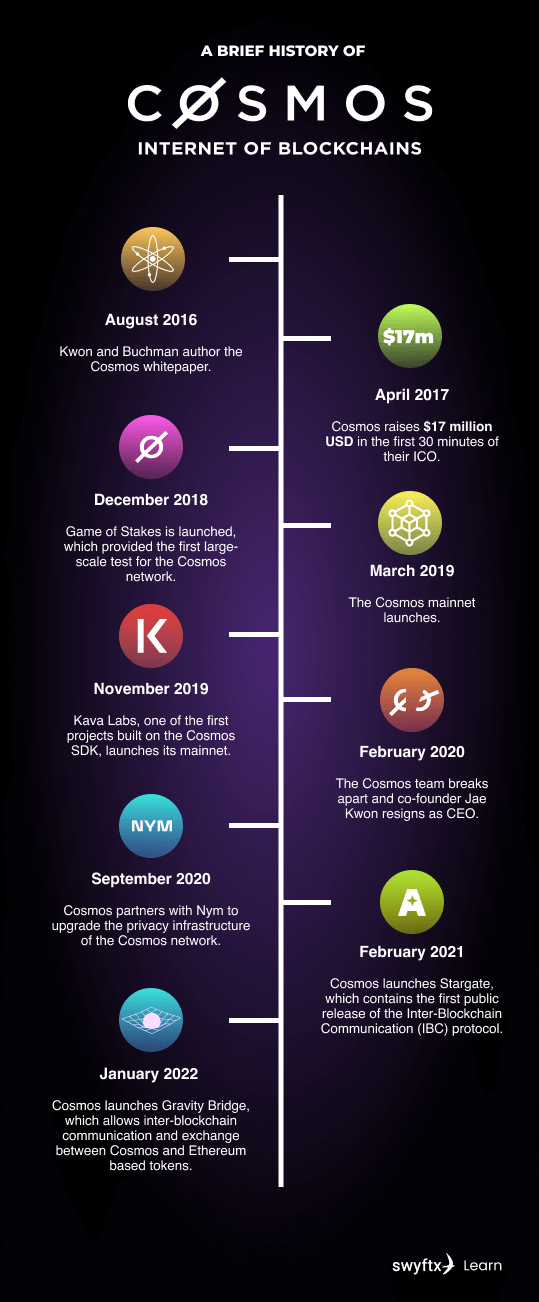
The development progressed steadily, with major milestones including:
- 2019: Launch of the Cosmos Hub mainnet (March 13)
- 2020: Release of the Stargate update, enabling IBC functionality
- 2021: Implementation of Inter-Blockchain Communication Protocol
- 2022-2023: Explosive growth in the ecosystem with numerous chains joining the network
Why Cosmos?
Before Cosmos, blockchain networks faced several critical challenges that limited their widespread adoption and utility. First, scalability was a major concern as single-chain architectures struggled to handle increasing transaction volumes. Second, the lack of interoperability between different blockchain networks created isolated ecosystems that couldn’t leverage each other’s strengths. Third, blockchain development requires significant technical expertise and time investment, making it difficult for developers to create specialized blockchain applications.
Cosmos addresses these challenges through its unique architecture and tools. The platform enables developers to create application-specific blockchains that can process transactions independently, solving the scalability issue. The Inter-Blockchain Communication Protocol (IBC) enables different chains to communicate and transfer assets, addressing the interoperability problem. The Cosmos SDK provides a framework that significantly reduces the complexity of blockchain development.
Understanding the Cosmos SDK
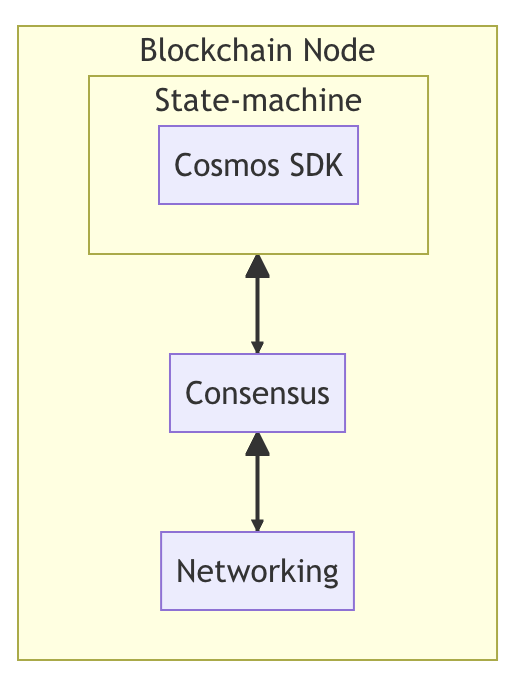
The Cosmos SDK is a framework that simplifies blockchain development by providing a modular architecture for creating application-specific blockchains. It’s built on top of Tendermint Core and provides developers with a rich set of pre-built modules that can be combined to create custom blockchain applications. At its heart, Cosmos is built on four primary elements: Tendermint BFT, the Cosmos SDK, the Inter-Blockchain Communication Protocol (IBC), and the concept of Application-Specific Blockchains.
The SDK follows a modular approach where each piece of functionality is encapsulated in a module. These modules can handle various aspects of blockchain functionality, such as:
- Account management
- Token transfers
- Staking and delegation
- Governance
- Custom business logic
This modular design allows developers to reuse existing modules while having the flexibility to create custom modules for specific use cases. The SDK also provides important security features and standardized interfaces that ensure compatibility across the Cosmos ecosystem.
Tendermint BFT Consensus Mechanism
Tendermint is the backbone of the Cosmos network, providing a Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) consensus mechanism that ensures network security and consistency. Unlike proof-of-work systems used by Bitcoin and Ethereum, Tendermint uses a proof-of-stake approach that is more energy-efficient and capable of higher transaction throughput.
The consensus process in Tendermint occurs in rounds, where validators take turns proposing new blocks and voting on their validity. Each round consists of several steps:
- Propose: A validator is selected to propose the next block
- Prevote: Validators vote on the proposed block
- Precommit: If more than 2/3 of validators prevote for the same block, they precommit
- Commit: If more than 2/3 of validators precommit, the block is added to the chain
This process ensures quick finality (typically within seconds) and provides strong security guarantees as long as less than one-third of validators are malicious. Tendermint is software for securely and consistently replicating an application on many machines. That means that Tendermint works even if up to 1/3 of machines fail in arbitrary ways. Every non-faulty machine sees the same transaction log and computes the same state. Secure and consistent replication is a fundamental problem in distributed systems; it plays a critical role in the fault tolerance of a broad range of applications, from currencies, to elections, to infrastructure orchestration, and beyond.
Inter-Blockchain Communication Protocol (IBC)
The Inter-Blockchain Communication Protocol is perhaps the most groundbreaking innovation within the Cosmos ecosystem. IBC enables sovereign blockchain networks to transfer tokens and data while maintaining their independence. It’s not just a token bridge – it’s a standardized protocol for inter-blockchain communication that handles authentication, transport, and ordering of data packets between chains.
IBC operates through a system of relayers that monitor the state of connected chains and facilitate the transfer of messages between them. The protocol ensures that:
- Messages are authenticated using light client verification
- Packet delivery is reliable and ordered
- Cross-chain transactions maintain atomicity
- Chain sovereignty is preserved
The protocol supports various types of cross-chain interactions, from simple token transfers to complex multi-chain smart contract calls, making it a powerful tool for building interconnected blockchain applications.
Application Specific Blockchains (App Chains)
Application-Specific Blockchains represent a fundamental shift in how blockchain applications are built. Instead of deploying smart contracts on a general-purpose blockchain, developers can create entire blockchains optimized for their specific applications. They are customized to operate a single application, instead of building a decentralized application on top of an underlying blockchain like Ethereum, developers build their blockchain from the ground up. This also means building a full-node client, a light client, and all the necessary interfaces (CLI, REST, …) to interact with the nodes. There are several advantages to app chains:-
- Performance: App chains can be optimized for specific use cases, leading to better performance
- Sovereignty: Applications have complete control over their consensus mechanism and governance
- Flexibility: Developers can implement custom features that might not be possible on general-purpose chains
- Scalability: Each app chain processes its own transactions independently
This concept has led to the creation of numerous specialized chains within the Cosmos ecosystem, each serving specific purposes while maintaining interoperability with the broader network. Example: Flare, Secret Network, Akash Network, etc.
Cosmos Hub (ATOM)
The Cosmos Hub is a public Proof-of-Stake chain that uses ATOM as its native staking token. It is the first blockchain launched in the Cosmos Network and developed using the cosmos-sdk development framework and ibc-go. It is also the first security aggregation platform that leverages the interchain-security protocol (ICS-28) to facilitate the launch of cosmos-sdk blockchain projects. It acts as a service provider for other chains and a coordination point for inter-chain communication. The Hub’s native token, ATOM, serves multiple purposes:
- Securing the network through staking
- Participating in governance
- Paying transaction fees
- Providing economic incentives for validators
whereas the HUB was built to act as an intermediary between all the independent blockchains created within the Cosmos network, called “zones.” In Cosmos, each zone is able to carry out its essential functions on its own. This includes authenticating accounts and transactions, creating and distributing new tokens, and executing changes to its own blockchain. The Cosmos Hub is tasked with facilitating interoperability between all the zones within the network by keeping track of their states. It not only facilitates interoperability but also provides shared security services to other chains, acts as a coordination point for cross-chain applications and support governance decisions that affect the entire ecosystem as a whole.
Zones and Hubs Architecture
The Cosmos network employs a hub-and-spoke architecture where multiple independent blockchains (zones) connect to central hubs. This architecture allows for:
- Scalability through parallel processing of transactions across multiple zones
- Flexibility in chain design and governance
- Reduced risk through compartmentalization
- Efficient routing of inter-chain communications
Zones are sovereign blockchains that handle their own governance and consensus while maintaining IBC connections to hubs. Hubs act as routers and facilitators of inter-zone communication, enabling zones to interact without requiring direct connections between each pair of zones.
Validators and Delegators
The security and operation of Cosmos networks rely on two key groups of participants: validators and delegators. Validators are responsible for maintaining the network by:
- Proposing new blocks
- Voting on proposals
- Maintaining network security
- Running reliable infrastructure
Delegators are token holders who contribute to network security by delegating their tokens to validators. This system allows for broader participation in network security while maintaining efficient consensus. Delegators earn a share of transaction fees and inflation rewards, minus a commission taken by validators.
Staking Mechanism
The staking mechanism in Cosmos is central to its security and governance model. Through staking validators and delegators lock up ATOM tokens as collateral while the network selects validators based on their total stake. The participants earn rewards for contributing to network security and any sort of malicious behavior can be punished by slashing. The staking mechanism creates strong economic incentives for network participants to act honestly and maintain network security. It also provides a source of passive income for token holders who delegate their tokens to validators keeping the community motivated to contribute to the ecosystem.
Conclusion
The Cosmos ecosystem represents a significant evolution in blockchain technology trying to solve challenges of scalability, interoperability, and usability. The ecosystem is constantly evolving with more and more application-based blockchains coming up. The combination of application-specific blockchains, the Inter-Blockchain Communication Protocol, and the proof-of-stake consensus mechanism creates a powerful platform for building the next generation of blockchain applications. Read more about the ecosystem in their official documentation.
