Table of Contents
Introduction
Monad Blockchain is on the cusp of being a revolutionary Layer 1 blockchain platform, set to transform the scalability and efficiency of decentralized networks. As we dive into the workings of this new technology, we’ll look at its architecture, performance capabilities, and possible applications that distinguish it in the world of blockchain.
What is Monad Blockchain?

Monad is an EVM-compatible Layer 1 blockchain that aims to solve the scalability trilemma by delivering high performance without compromising on decentralization or security. It is intended to facilitate the easy redeployment of EVM-equivalent bytecode to maintain full compatibility with Ethereum’s opcode and gas mapping standards. Read about it in depth here.
Monad Blockchain’s primary characteristics are:
- 10,000 transaction per second (TPS) throughput
- 500 ms block times with finality in 1 second
- Full EVM compatibility for uninterrupted migration of Ethereum dApps
- Feeless transactions
- Low hardware costs for node operation
Monad’s Breakthrough Architecture
Consensus Mechanism: MonadBFT
MonadBFT underlies Monad’s architecture, a non-public Byzantine Fault Tolerance consensus algorithm based on HotStuff. This mechanism streamlines communication among validating nodes by reducing consensus rounds from three to two, thereby increasing efficiency and enabling faster block creation.
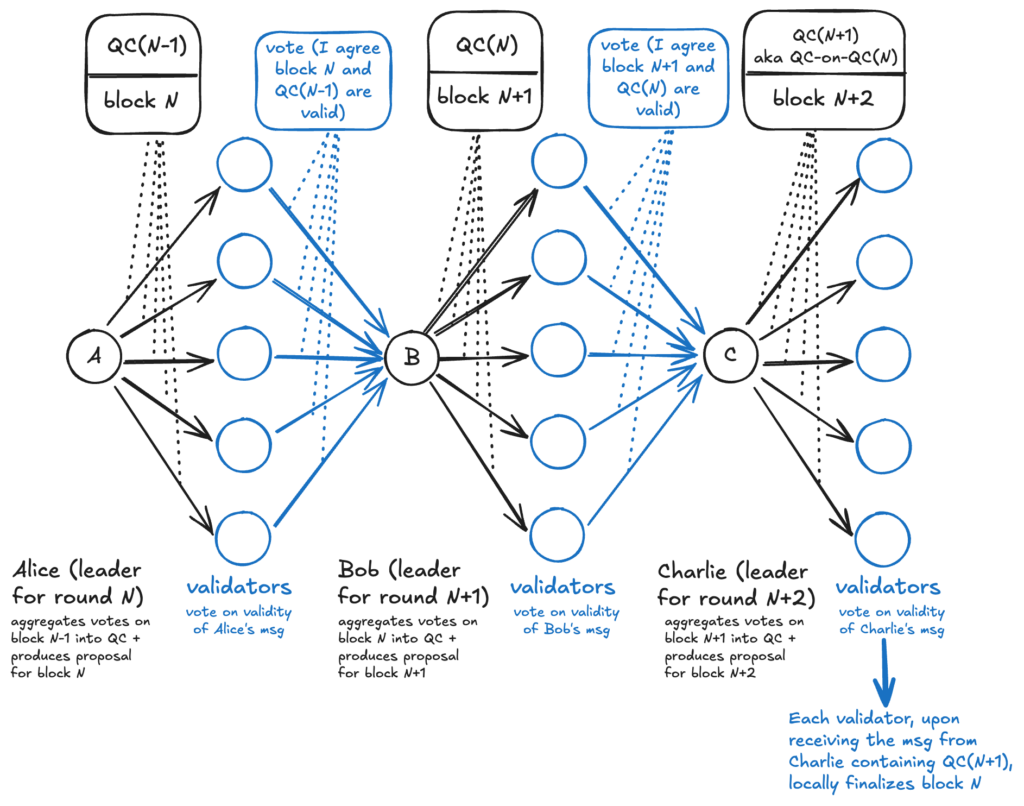
Parallel Execution Model
Monad employs an optimistic parallel model of execution that significantly enhances transaction processing speed. Unlike blockchains where transactions are processed sequentially, Monad processes all transactions to be executed independently concurrently. When dependencies exist, it re-executes the concerned transactions on the basis of fresh data.
MonadDB is a database specifically optimized for parallel execution. It has Patricia Trie data structures on disk and in memory, with low-latency asynchronous read/write access. This innovation enables high-throughput transaction processing and reduces memory requirements for operating nodes.
Node Architecture
Every Monad node consists of three primary components:
- monad-bft: Consensus
- monad-execution: Transaction execution and state transition
- monad-rpc: User read/writes
Comparison with Other Blockchains
Monad’s architecture has several advantages compared to other blockchain platforms. To understand Monad in comparison with other prominent Layer 1 blockchains, the following comparison table is presented:
| Feature | Monad | Ethereum | BNB Chain | Avalanche | Solana |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Consensus Mechanism | MonadBFT | Proof of Stake | Proof of Staked Authority | Avalanche Consensus | Proof of History |
| Transactions per Second (TPS) | 10,000 | ~15-30 | 60-100 | ~4,500 | ~65,000 |
| Block Time | 500ms | ~12 seconds | ~3 seconds | <1 second | 400ms |
| Finality | 1 second | ~12 minutes | ~1 minute | <2 seconds | ~13 seconds |
| EVM Compatibility | Full | Native | Full | Full | Partial (via Neon EVM) |
| Gas Fees | Near-zero | Variable, often high | Low | Low | Very low |
| Smart Contract Language | Solidity | Solidity | Solidity | Solidity, C-Chain | Rust |
| Parallelization | Yes | No | No | Yes (Subnets) | Yes |
| Decentralization | High | High | Moderate | High | Moderate |
| Scalability Approach | Parallel execution, MonadDB | Layer 2 solutions | Larger block size | Subnets | Parallel transaction processing |
Based on the table, we notice that Monad Blockchain boasts several exclusive advantages:
- Performance: Monad’s 10,000 TPS leaves far behind Ethereum’s ~15-30 TPS and BNB Chain’s 60-100 TPS. While Solana boasts higher TPS, it is at the cost of decentralization and complete EVM compatibility.
- Scalability: Monad’s parallel execution and optimized data structures allow for better scalability compared to sequential processing chains like Ethereum and BNB Chain.
- Decentralization: Unlike some high-performance chains that are founded on extensive node requirements, Monad maintains decentralization through its optimized design and low hardware requirements.
- EVM Compatibility: Monad has full bytecode compatibility with EVM, and Ethereum applications may be migrated with no code changes, such as BNB Chain and Avalanche but superior to the partial compatibility of Solana.
- Low Fees: Near-zero gas fees of Monad are as good as Solana’s extremely low fees, a tremendous improvement over the often high and volatile fees on Ethereum.
Applications and Use Cases
Monad’s high performance and low fees make it a suitable solution for a wide range of applications:
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Monad’s architecture is well-positioned for DeFi applications, especially those involving high-frequency trading and deep liquidity pools. The ability of the platform to handle thousands of transactions per second at near-zero costs can significantly enhance the efficiency of decentralized exchanges and lending protocols.
NFT Marketplaces
The minimal cost of transactions and maximum throughput make Monad an ideal choice for NFT marketplaces. It has the capability to handle large numbers of transactions without network congestion which is typically seen on other chains during popular NFT sales or mints.
Gaming and Metaverse Applications
Gaming and metaverse applications require fast and reliable processing of transactions. The concurrent processing by Monad ensures lag-free game experiences and easy virtual world interactions.
IoT and Supply Chain Management
The effectiveness of Monad blockchain makes it able to handle the high volume of transactions generated by IoT devices in supply chain management systems. Its high throughput and low latency are able to maintain real-time tracking and management of large-scale IoT networks.
Decentralized Social Media
Monad’s performance can make decentralized social media platforms with millions of users and interactions possible. Its high performance can handle the constant stream of data and transactions typical of social networking programs.
Conclusion
As Monad Blockchain prepares for its testnet launch on 19th February 2025, it has already garnered significant interest from developers and investors. The platform’s innovative approach to the problem of blockchain scalability positions it as a strong contender to revolutionize the industry. With its combination of high performance, EVM compatibility, and decentralization emphasis, Monad is a significant breakthrough in blockchain technology. As the ecosystem develops, we can expect numerous various applications leveraging Monad’s capability, possibly revolutionizing the landscape of decentralized applications and Web3 services.