Table of Contents
What is nonce in blockchain?
Nonce is an abbreviation for “number used only once” or “number once”. It is a random number that the Bitcoin mining program uses. Nonce is included in the header block and then that number is hashed. Suppose the result of the hashed information i.e. a hexadecimal number adds up to a value of less than or equal to the Bitcoin network’s difficulty target. In that case, the miner’s block gets added to the Bitcoin Blockchain. Another block gets opened and the process continues.
Key Takeaways:
- A nonce in blockchain is a random or as some argue, a semi-random value, which is used to ease the cryptographic communication process. It is also used to authenticate cryptographic hash functions which is why it is sometimes referred to as a cryptographic nonce.
- In a blockchain, a block consists of four important pieces of information – transaction data, nonce, the hash value (an alphanumeric value that is used to identify a block) of the current block, and the hash value of the previous block. A nonce can only be used once.
- The Nonce in blockchain is one of those parameters that can be changed to compete in the mining process.
- Finding the right combination of Nonce and other values in a block takes significant computing power in mining.
Understanding the Nonce in Blockchain
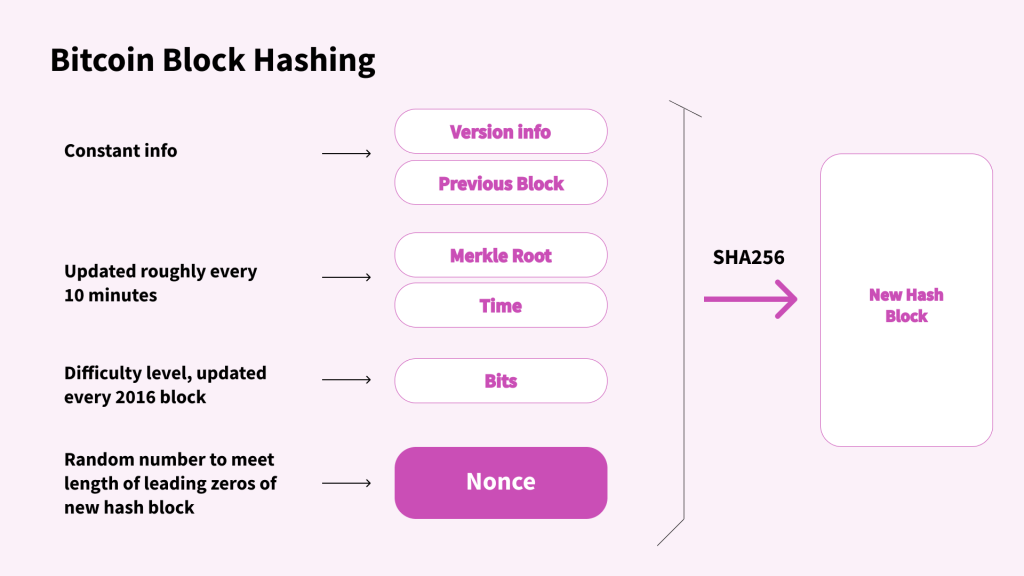
Bitcoin Nonce is a 32-bit (4-byte) number used by miners to try and generate a valid hash for creating a new block on the Bitcoin blockchain.
The Nonce field included in the block header includes the following attributes as well:
- The software version
- The previous block’s hash
- A timestamp
- The difficulty target
- The Merkle root
Let us break down the workings of a nonce so that you have an adequate understanding of what this randomly generated number does. All the blockchains in the world today work on a specific consensus mechanism. There are two main consensus mechanisms – Proof-of-Work (PoW) and Proof-of-Stake (PoS).
Proof-of-Stake does not have anything to do with the Nonce number. A nonce is generated only in those blockchains that support a Proof-of-Work consensus system.
In a Proof-of-Work consensus system, miners who are individuals responsible for verifying transactions by solving complex mathematical problems select a nonce value. This is done to use this value as a base for a hashing algorithm which is used to authenticate data. Now, you may wonder if it’s about selecting a random number, any person who is good with numbers and mathematical methods will be able to solve this in a second. Well, there’s a catch. The miners in a Proof-of-Work consensus mechanism are given a target that either has 2 leading zeroes or 3 leading zeroes and it is revised after every 2016th block.
So, when the random value, that is nonce as a 32-bit number, is put through the hashing algorithm, the resultant number must abide by a certain difficulty level or target value specified by the blockchain to be approved.
In one line, the function of a nonce is to be used as a base or as an anchor to generate a hash value for a particular block in a blockchain. The miners, thus, must crack the nonce to generate a hash value that will eventually become the identity of a block. This is what a nonce means in crypto and also how it helps a blockchain.
What is Hashing?
Hashing is a process in cryptography where a piece of information (number or text) is passed through a mathematical function to generate a new value called a hash value. The cryptographic hash function (mathematical operation) takes block data into the function and encrypts it by converting the value into a unique out of hexadecimal characters with fixed length.
This hash value can be seen as a fingerprint of the block which is unique to every block on the blockchain. The nonce is the only variable in the block header that miners can change/modify. By randomly changing the nonce miners change the hash of the block and calculate various possible solutions.
In the Bitcoin blockchain, the SHA256 hashing algorithm is used.
Nonce Meaning in Blockchain
In layman’s terms, a nonce can be defined as a random number used only once. This random number is used in different computer systems of which cryptography is an integral part.
When it comes to a specific block of a blockchain, this randomly generated value that we call nonce is combined with a hashing algorithm that takes input data and generates a fixed and immutable number that we call hash. Hash is a unique number that serves as the identity of a block in a blockchain.
Once a miner has cracked the nonce value, they would put all the data of a block which includes the number of transactions, timestamps, etc. into the hashing algorithm along with the nonce value. The result of this will be the value that must meet a specific threshold which is the difficulty level in a blockchain.
What is The Purpose of Nonce in Blockchain
By now, you must have had some idea of the sheer importance of nonce and how big of a role it plays in a Proof-of-Work blockchain. Here is a breakdown of some more important features of a nonce value.
- Nonce in blockchain helps create an immutable, tamper-proof ledger in the blockchain.
- Double-spending is a big threat in the blockchain which can potentially jeopardize a chain of blocks. Therefore, nonce in blockchain also helps prevent such attacks.
- Blockchain is essentially a decentralized system. To make sure that it is fair in its workings and outcomes, all the miners have equal chances of finding a nonce value. This way, they also protect the essence of a blockchain – its transactions.
- Finding nonce in blockchain is a rigorous process. Only those who are sincere and up for the challenge are allowed to generate a nonce value.
Can I generate a nonce value in blockchain?
While it is a little difficult to say who can generate a nonce value and who cannot, it is important to understand the basic steps that one must follow to crack the puzzle and generate a valid nonce in blockchain.
Step 1
The very first step involves selecting a block of unconfirmed transactions.
Step 2
Once the miner has chosen a block, they are required to create a block header that includes the hash of the previous block, the timestamp of the new block, and the number of selected transactions in the form of a list.
Step 3
The miner then selects a random number and puts it through a hashing algorithm. This will generate a hash value.
Step 4
Now, if this value meets the difficulty criterion or the target threshold, the block is approved but if it does not then the miner will have to keep trying.
Nonce-related attacks to be aware of
Like anything in the world, the nonce in blockchain is also not immune from being attacked by hackers. Here is a list of nonce-related attacks that you must keep in mind and take necessary precautions against.
1. Reusing the nonce in blockchain
This happens when an attacker, an imposter, or a hacker uses the same nonce value as a legitimate user to verify a block, disrupting the whole blockchain. Nonce can not be used the second time. The hackers and attackers who reuse the nonce value steal the data and make it readily available online, jeopardizing the security and identities of the users.
2. Impersonating the legitimate user
In this particular case, a hacker or an attacker would wait and try different nonce values to generate a solid hash value. Once they have found a nonce that generates the same hash value as someone with a slightly different nonce value, they would impersonate the legitimate user and pretend to be them.
3. The researcher’s punch
This particular attack requires a lot of extensive and in-depth research. In this case, a hacker would try different combinations of nonces unless they have found a valid value. This is not too common an attack because it is both expensive and requires a lot of brain drain.
4. Passing the nonce
This is an interesting case. In this attack, a hacker would intervene between a process of a nonce value and would quickly slide in their own generated nonce value which would lead to the block being verified to their name and not the original user’s name.
In conclusion, a nonce is an essential element in cryptographic protocols that helps to ensure security and prevent various types of attacks.
