Table of Contents
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) represents a new era of artificial intelligence (AI), where a machine will be able to mirror human-like intelligence and also have the ability to self-teach. The type of AI that is the most prevalent today is narrow AI. While Narrow AI systems are designed for specific tasks such as language translation or image recognition, the goal of AGI is to essentially perform any task as well as a human being can.
What is AGI?
AGI is also known as “strong AI” or “full AI”. It is an AI system that is capable of understanding, learning, and applying knowledge across a wide range of tasks without being limited to one particular domain. As the name suggests, it would have the capacity for generalization: taking what it has learned in one context and applying it to another. This would make it capable of reasoning, planning, problem-solving, and even exhibiting common sense much like we do as humans, and even allow it to do tasks that it has not seen before.
Ultimately, the goal is to reach intelligence that supersedes humans in knowledge and ability, which is what we call the Artificial Super Intelligence of ASI. The diagram below compares the three types of AI that we have talked about so far.
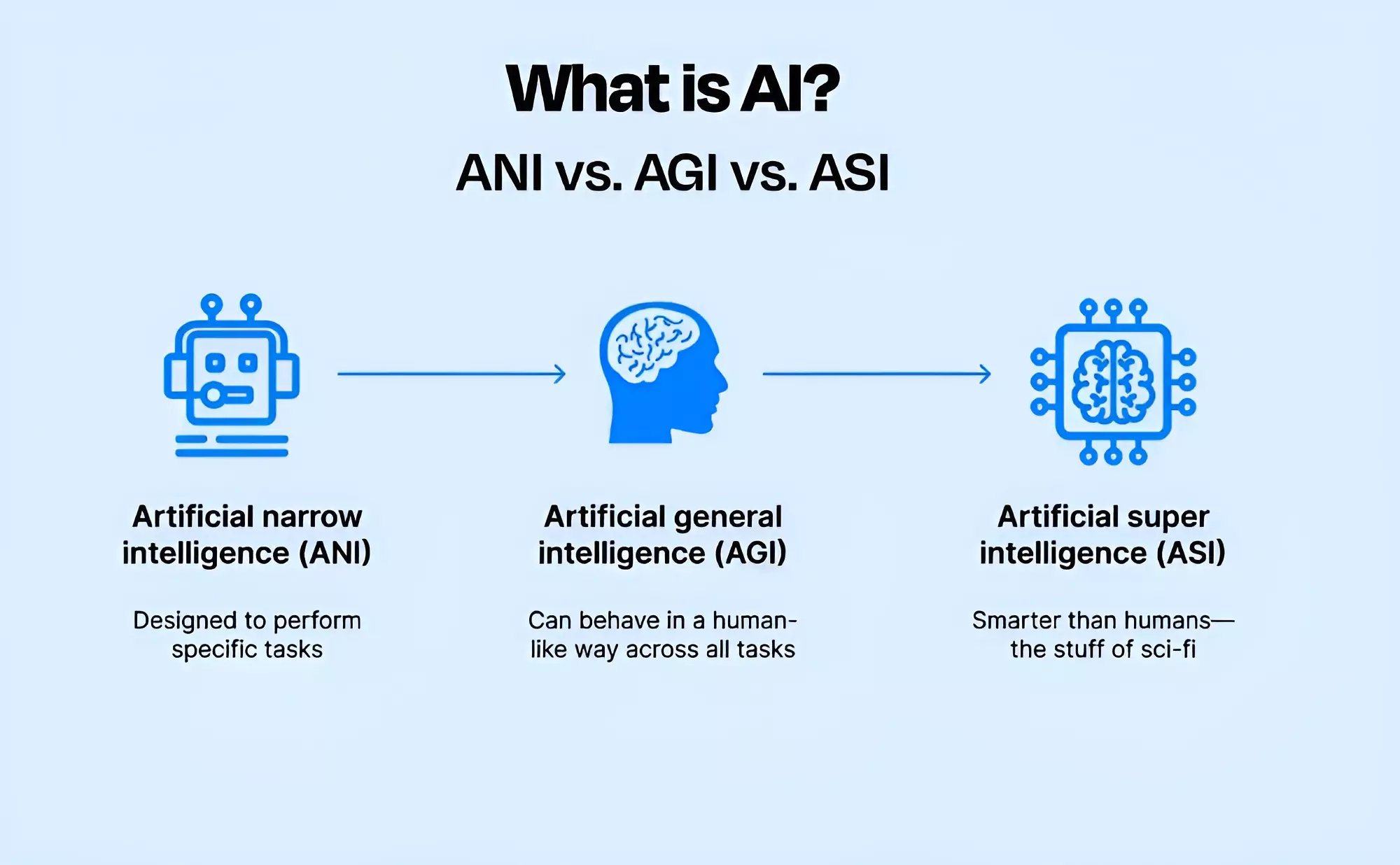
How is Artificial General Intelligence Different from Narrow AI?
Narrow AI is also known as Weak AI and basically refers to AI systems that are designed to perform a well-defined task or a set of tasks in a specific domain. These systems operate within a limited context and do not have any general intelligence or knowledge. They are only trained with a defined set of data that is necessary to achieve the set goal.
For example, a narrow AI system might be excellent at processing large volumes of data to predict stock market trends, but (if not trained to do so) it cannot use the same knowledge to also create charts to visualize the predicted data. This is because narrow AI systems lack the capacity to creatively apply the knowledge that they have across different domains—they can only do what they have been trained to do.
To learn more about narrow AI, check out this article.
On the flip side, Artificial General Intelligence would be able to integrate and analyze information from diverse fields, much like a human who can apply knowledge learned in one area to solve problems in another. Even if someone does not know how to create a chart for data visualization, to complete the task they will learn this new skill and then apply this new knowledge to pick a visualization tool and design a charts that can provide a visualization for the stock market trends—so will an AGI system.
Potential Benefits of AGI
The advent of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)—a form of AI that can understand, learn, and apply knowledge across a wide range of tasks at a human-like level—could bring transformative benefits across various sectors. AGI’s ability to process and analyze vast amounts of data, combined with its advanced reasoning capabilities, could make it a powerful tool for addressing some of the world’s most pressing challenges. For instance, it could model complex environmental systems to combat climate change, accelerate disease diagnosis and drug discovery in healthcare, and manage large-scale crises like natural disasters or pandemics by optimizing resource allocation and predicting outcomes.
Economically, AGI could drive significant growth by automating a wide array of tasks that currently require human intelligence, boosting productivity and efficiency across industries. It could handle everything from creative work like product design to strategic tasks like supply chain management, freeing up human workers to focus on higher-value activities. By reducing operational costs and enabling the creation of entirely new industries, AGI could spur economic expansion and innovation on a global scale.
AGI could also act as a catalyst for breakthroughs by augmenting human creativity and problem-solving capabilities. It could accelerate scientific research by analyzing vast datasets, identifying patterns, and generating hypotheses, leading to discoveries in fields like physics, biology, and chemistry. In the tech world, AGI could optimize algorithms, design hardware, and develop new software applications. Its ability to integrate knowledge from diverse fields could foster cross-disciplinary collaboration, unlocking solutions to problems that have traditionally been siloed within specific domains.
Additionally, AGI could revolutionize decision-making by providing deeper insights derived from the analysis of multifaceted data. In business, it could help leaders make more informed strategic choices by predicting market trends, optimizing operations, and identifying risks. In governance, AGI could support policymakers by modeling the potential outcomes of legislation, improving resource allocation, and enhancing public services. By combining data-driven analysis with human intuition, AGI could enable smarter, more effective decision-making at all levels.
Overall, the potential benefits of AGI are vast and far-reaching, offering solutions to global challenges, driving economic growth, accelerating innovation, and improving decision-making. While the development of AGI presents significant challenges, its transformative potential makes it one of the most exciting and impactful frontiers in technology and human progress.
Challenges and Risks
Despite its promise, AGI also comes with considerable challenges and risks. Let’s discuss some of them as well.
- Technical Complexity: Developing an AGI system that can match or exceed human intelligence involves overcoming enormous technical hurdles in understanding and replicating human cognition.
- Ethical and Social Implications: The deployment of AGI raises significant ethical questions, such as the potential loss of jobs, the need for robust oversight mechanisms, and the risk of unintended consequences if an AGI system acts in ways that conflict with human values.
- Security Concerns: AGI systems could become targets for misuse or cyber-attacks, and ensuring their safe operation will require advanced security protocols.
- Alignment Problem: One of the most critical challenges is ensuring that AGI systems’ goals align with human values and do not lead to harmful outcomes. This problem, often referred to as the “alignment problem,” remains a significant area of research.
Future Prospects
The journey toward AGI is filled with both exciting opportunities and formidable challenges. Researchers and technologists continue to make incremental progress by enhancing current models and exploring novel training methods, yet a fully realized AGI remains a long-term goal. As the field evolves, collaboration among academia, industry, and policymakers will be essential to steer AGI development in a direction that maximizes its benefits while minimizing risks. The potential for AGI to revolutionize industries and fundamentally alter the way we interact with technology makes it a critical area of focus for the future of artificial intelligence.
Conclusion
Artificial General Intelligence stands as a transformative vision for the future of technology—one where machines not only perform specialized tasks but also exhibit the flexibility and creativity of human intelligence. While significant hurdles remain, the pursuit of AGI promises advancements that could reshape industries, drive economic growth, and solve some of the most complex challenges facing society today. As research progresses, the conversation around AGI will increasingly focus on ethical governance, security, and alignment with human values, ensuring that this powerful technology benefits everyone.
By exploring the multifaceted aspects of AGI—from its definition and benefits to the challenges that lie ahead—we gain a clearer understanding of how AGI could redefine our world and what steps are needed to achieve this revolutionary goal.
Related Reading: